About Me
Michael Zucchi
B.E. (Comp. Sys. Eng.)
also known as Zed
to his mates & enemies!
< notzed at gmail >
< fosstodon.org/@notzed >

More Cell Tutorial
Part 3 of my Cell tutorial is up. Not much in this round, but more to come of course.
I've been doing pretty much SFA on hacking for the last week or so; the weather's turning to winter here and that always seems to such some enthusiasm out of you; at least for a bit. As did a few hang-overs and so has being stuck with writing documentation for so long.
People actually pay for this rubbish?
I was forced by the project manager to convert one of my documents into Microsoft Word format.
Wow, what an unpleasant journey this turned out to be. First the Lyx/LaTeX to ODF converter didn't work very well. Although I eventually got it to work on a GNUOS machine by removing some ps-tricks diagrams first. The text converted ok, but there were other problems. All the cross references were broken and needed to be fixed up, and the images needed re-inserting as they'd been re-sampled at a lower resolution.
Fighting with OpenOffice 'dot' org's nasty GUI features wasn't much fun. Such as the ones that have the screen bouncing around as you navigate through different document elements; often losing focus in the process -- navigating by keyboard was simply impossible. And finally, after getting the document to a decent state following one last change it simply refused to save in ODF format, so I was forced onto Microsoft Word.
So then came the less-than-perfect conversion to Microsoft Word format. It broke all of the references again. And inserted images, captions, and tables in a way which didn't work very well and needed to be re-done. Microsoft Word crashed twice just trying to re-arrange a table; and had the gall to make out that it was doing me a favour by (very) slowly ``recovering'' my work. Lots of issues with cross referencing (the cross referencing tool is worse than the OpenOffice 'dot' org one, and that's saying something), numbering, tables of contents, maths sections, styles, formatting, and even plain editing functions and the user interface. None of it worked well, and much of it barely worked at all.
Over-all, a few days of a head-ache inducing and hair-greying experience I hope not to repeat any time soon. At least OpenOffice 'dot' org has an excuse, it doesn't cost anything. Although the claimed interoperability is simply not there; but we all know who to blame for that. But someone paid for this Microsoft Word, and it is an utterly ghastly horrible product that only produces amateurish results when it does manage to do what you ask it to.
After having written the document originally using Lyx, and having recently worked with Texinfo as well, even their combined quirks and difficulties pale in comparision to these utterly unproductive, rubbish tools.
Introduction to CBE, Part 2 (chapter 3)
I've uploaded the second part of my Cell BE intro up toEverything Cell. Things are a bit more interesting this time and it gets straight into talking about double-buffered DMA and SPUs and registers and other fun stuff. Should be enough to digest until the next chapter which gets into multi-processing.
Whilst checking that it uploaded ok I did some proof-reading and realised the writing style isn't terribly good. If wordpress didn't force html line breaks all over the place it would look a bit better too. My excuse is that it's only a draft and i'll keep working on it as I have time.
Although now i've got this out of the way i've gone back to playing with some of my Java projects for a while. Oddly enough, using wordpress has given me inspiration to work on my own internet publishing tool again; although it also shows just how far off my ideas are of being realised too.
National Broadband Network
Wow, so Ruddy and Crew want to build a fibre-to-the-home network for the whole of the country through a publicly sponsored company. Well since nobody else would do it, I guess they had no choice, and It's about time we jumped into the 21st century. We've been held back too long by abusive behaviour from our local telephone monopoly.
All the 'pundits' keep focusing on the impact on phone companies and ISPs ... Far too narrow a view -- I think for example that if I was a free-tv television broadcaster I'd be somewhat more worried than anyone else right now.
One negative is that this is the same government who wants to censor the internet. That's a major negative.
Introduction to CBE
Aren't we spoilt today, two posts in a few hours.
Just a quick mention that I've started publishing my introduction to Cell programming - based on the Mandelbrot generator I wrote last year and a few other bits and pieces.
It's on a new site Everything Cell which is a tad bare at the moment, but will hopefully tie together some cell programming resources for free software developers and hackers interested in programming on the PS3 and the CBE CPU.The first chapter is a bit unexciting but sets up some framework before I can get into the nitty gritty. It's surprising just how much work it is getting this stuff together.
PS I cleaned up the theme here too.
Free Software Inspiration
What inspires people to write free software? It isn't psoryisis or insufficient hygiene as some have appeared to claim.
Self Education
Self education is a significant driver of contributions to free software. There is no better way to learn about something simply to do it. Free software has been built with education in mind; all the source, the documentation, the tools, even the operating system is available to all for no cost and with few restrictions. Good quality documentation and manuals are a core part of the free software eco-system.
In addition there are other ways in which computer software itself is an ideal self-education persuit:
- Interactive languages which provide instant feedback.
- Many languages and environments to choose from.
- Integrated documentation.
- Mistakes are cheap. No raw materials are consumed.
- Mistakes are also safe, and private.
- Knowledge is free. It only costs you the time to aquire it.
- Can be done in complete isolation as well as socially.
As a student or professional, contributing to free software can be a great way to learn about a new area or keep up with technology. It costs nothing but your time and you gain not only knowledge but may end up with a useful tool or application from your efforts in addition to the knowledge gained. It also provides a public portfolio of your work that may aid your career (it should be worth more to an employer than a paid-for certificate).
Entertainment
Writing software can be incredibly fun. Learning new things in itself is quite a fun activity, but even simple things like getting a Makefile working nicely is a little spot of joy -- at least until you move onto the next problem.
I like to compare it to a polymorphic Rubik's Cube. No matter how many times you solve one part of the puzzle there will always be more puzzles to solve. It is a never-ending journey with little victories at every stage. Like the adventures of Monkey the journey is important, not the destination.
Of all the thousands of dollars i've spent on entertainment such as movies and games, I would only have experienced a tiny percentage of enjoyment in a far smaller period of elapsed time than compared to simply writing software.
Unfortunately releasing your software efforts to the world can destroy the entertaining aspect. Once you have users you also have complaints and bug reports, and although these can be ok for a time they can quickly get out of hand. More so recently as there are increasing numbers of less-skilled users likely to be using your software.
Personal Psychology
Perhaps it is for the approval of others, or simply to assert that you exist as an individual in a modern world, or that you belong to or lead a desirable group.
I think this must be quite a factor in many peoples decision to take part in free software projects rather than keep their efforts private. For example, projects don't have ``programming teams'' and ``users'' anymore, they have developer and user ``communities''. I don't really like the term, and find it devalues the original meaning -- much like a facebook ``friend'' does.
Need
Need is the major driver for most software full-stop. So it must necessarily be a major driver for free software. Some developers simply release their code as free software as a matter of course, regardless of whether others might find it useful. Others attempt to leverage the skills and time of others to improve and maintain a project. But in either case the software was written in the first place simply because it was needed, and it's development has already been paid for.
Unfortunately, most needs-based software stays locked up in individual organisations or machines until it ages beyond repair and is replaced by more of the same.
Politics
Obviously the free software movement is a political one. It strives to produce a completely free software computing environment for all users. It is about empowering users as much as it is about empowering developers, and it intentionally blurs the line between the two. Being able to programme a computer is not a secret that is only to be shared amongst the priviliged few -- it is an activity anybody can partake in. And one everyone must be allowed to partake in should they choose to.
Although I believe strongly in this ideology, I do find it quite difficult to use it as a sole source of inspiration. I've downloaded several ``high priority projects'' from the GNU project and looked at the source, but I usually just end up with a sinking realisation that I just can't get committed to any of them.
Ego
Lets face it, you're a better programmer than most -- I know I am!
So when you're using a piece of software that sucks, you always know you can do a better job. And there's no better way to put your money where your mouth is than show it off to the world in a free software project.
Although it probably took me a while to realise it, this is really what inspired me to join the GNOME project in the first place, and is driving me in my latest interests as well. There is some very poor software out there, and thus a great deal of potential inspiration.
Sore throat, sore fingers, sore head, sore heart.
I had a party for a friend visiting from Chicago last week. Drank way too much of course. Not bad for a school night, although I planned ahead and took the day off. Then I caught a bad cold or a mild flu off a house-mate, and got stuck with that over the whole bloody weekend.
Over that same weekend I worked on an introduction to Cell B.E. programming. Quite a lot. A series of worked examples starting from a plain C Mandelbrot generator, through various phases of SPUification and SIMDisation up to a final high performance(?) implementation. And all the trials and tribulations, discoveries and tricks along the way. I'm looking to publish a chapter a week or so to a new free software Cell hacking site that will hopefully come together soon. I wrote it using texiweb, using literate programming. Eight postable chapters plus introduction and appendices so far, and there are still plenty of ideas to explore.
And to top it off, yesterday I was cooking some meat on the BBQ, and I wanted to check the flame setting -- which tends to involve looking under the front. I didn't notice the folding chair right where my head was heading to, so I got a rather heavy bump on my forehead that seems to hurt more now than it did at the time.
After the party and flu I finally went to work today but I think I could've done with another day off. Apart from not being fully past the virus, it feels as though I'm suffering withdrawal from all the hyper-active hacking I've been doing on the couch over the last few days. Empty heart, irritable disposition, and feelings of exhaustion and despair.
Layout via Optimisation
Since I mentioned linear programming in the last entry I've managed to wrap my head around it enough to come up with a possible solution for my layout issues.
Example layout problem:

If I just consider the horizontal coordinates, the following known values and relationships describe this layout:
B centre = A centre
B width = 40C width = B width / 2
C left = B right + 5D width = 100
D right = B rightWant to know:
Left and right of every box.
Now a recursive layout algorithm has trouble with this. It can't determine the offset of B without knowing the size of A, but the size of A depends on the offset of B. You need to do at least a couple of size and layout passes, and even then I'm having trouble getting it working (and I don't have the perserverance to keep trying).
It seems at first that solving the simultaneous equations would work. But in general this isn't useful because there is nothing to stop negative widths being created -- which isn't terribly useful. And determining enough additional terms to constrain the solution (e.g. that D left = A left) requires calculation itself.
Changing this to an optimisation problem allows it to be defined without the need for it to be fully specified. And constraints keep the values pointing the right way.
After a bit of fiddling about, I think I've come up with a basic systematic procedure which should allow the determination of the results using the simplex algorithm. It may not be the most optimal setup, but it appears to be relatively robust so far.
- Trivially define the objective function in terms of the sum of every left and right X coordinate.
- Define width relationships - the known knowns, or the known unknowns.
- Define container constraints - every child is fully inside its parent. Unless the parent size is defined explicitly, in which case do not add any implicit relationship.
- Define layout constraints.
Applied to the problem above, first, trivially define the object function in terms of the left and right bounds of every box:
p = ar + al + bl + br + cl + cr + dl + dr
This is a minimisation problem in p.
Next define the widths:
br - bl = 40
dr - dl = 100
ar - al >= 0
cr - cl >= 0 (since we know this is B width / 2, we could just use 20 too)
Define the container relationship -- everything inside A must be inside A:
br - ar <= 0 cr - ar <= 0 dr - ar <= 0 al - cl <= 0 al - bl <= 0 al - dl <= 0 Everything is relative to A, so set A's left edge to 0, so it doesn't float up to meet the highest other boundary. al = 0 Now define the layout relationships. B centre = A centre bl + (br - bl)/2 = (ar - al) / 2 or bl/2 + br/2 - ar/2 + al/2 = 0 C width = B width / 2 cr - cl = (br - bl)/2 or br/2 - bl/2 - cr + cl = 0 C left = B right + 5 cl = br + 5 or cl - br = 5 D right = B right dr = br dr - br = 0 And running the simplex method over this system generates everything I need directly: Optimal Solution: p = 650; ar = 160, al = 0, bl = 60, br = 100, cl = 105, cr = 125, dl = 0, dr = 100 (calculated using http://www.zweigmedia.com/RealWorld/simplex.html) Nice. And just as a test, lets shrink D to be smaller than B, say 30.
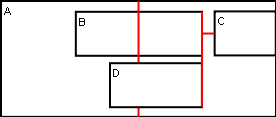
Optimal Solution: p = 440; ar = 90, al = 0, bl = 25, br = 65, cl = 70, cr = 90, dl = 35, dr = 65
Still works.
It should be able to calculate both dimensions and deeper structures simultaneously. This will allow relationships across dimensions, e.g. A width = B height * factor + offset.
One thing the recursive layout routine handled ok was affine transforms (after a lot of mucking about mind you). I guess this should handle them too if I get the coordinate space correct. Relative position calculations need to be in parent space, but the layout calculations need to be in global space.
Now I just have to work out how to calculate those parameters from expression trees, and find out if a solver will run fast enough. Actually I'm pretty confident of the performance question, even a trivial implementation I wrote for work did thousands of rows and columns in a few hundred ms.
Copyright (C) 2019 Michael Zucchi, All Rights Reserved.
Powered by gcc & me!


