About Me
Michael Zucchi
B.E. (Comp. Sys. Eng.)
also known as Zed
to his mates & enemies!
< notzed at gmail >
< fosstodon.org/@notzed >

Improved post navigation links
I've made a minor improvement
to blogz so that when viewing a
single post the navigation links at the bottom of the post show
the title of the next/previous post rather than just saying 'Older'
or 'Newer'. This was something I had intended to add when I got
the database backend working but that is still in limbo. Actually
most of the code for the blog output is done, I just can't decide
on relatively unimportant details like the serialisation format
for the metadata records. The other issue is adds a whole mass of
potential complexity to creating posts rather than just editing a
file on a shell login. Like an order of magnitue of complexity.
It doesn't require this complexity but it enables it.
I made some other minor changes to the stylesheet mostly to do
with inline figures (photos and captions), justified the text of
posts, and messed about with the About box.
Reading multi-stream high-depth videos in octave (and matlab)
So I discovered recently that octave and matlab support direct
calling out to Java. We had a need to read both multi-stream and
high bit-depth videos from them, and using jjmpeg seemed a lot
easier than writing some mex shit. The native video format
support in matlab is abysmal and it simply has no capability for
reading multi-stream videos either.
Anyway, i've just commited some stuff to jjmpeg
in contrib/octave.
It consists of a simplified multi-stream VideoReader and a small
set of octave.m files which ease it's use and make it portable.
And a Makefile to compile this using a Java 8 JDK because those
tools are so wildly out of date.
The .jar file and octave scripts are portable to matlab.
Althhough the license means they cannot be distributed, I think.
Since the freenect2 indev patches were not accepted into ffmpeg I
will add them and probably the kinect2 indev patches to
jjmpeg/contrib as well. At some future point in time.
ZedZone sitemap.xml
I've added a sitemap.xml to the site.
Maybe that'll make google consider adding it to it's index as it's
only indexing 130 odd pages out of 1K+. bing is probably a lost
cause, it's only indexed 10 pages.
It's a
patch to blogz which
generates both the short (id only) and long (date-title) urls as
well as a sitemap for the few plain html articles which mostly
cover the project home pages.
I also noticed some very old url's were being accessed so I added
a redirect from /blog?post=xx to /post/xx. Huh now i think of it
/blog?post=xx was blog by date, but no matter, it's good enough.
Been a bit sick and not really on top of it the last few days.
incremental javac, make
I've been looking into incremental javac compilation again. I had
most of the code for one approach done weeks ago but it never
really got to the point of doing anything useful.
The goal is to simplify a GNU make based Java build system while
ensuring consitent and complete builds.
javac -m <module> comes very close to what I
want but the main problem is that it doesn't remove stale files.
These come about for the same reasons that might occur with C
development, for example the .java file is renamed or deleted.
But there are many more cases that occur regularly in Java, for
example an inner class or anonymous inner class is removed or
renamed. And in C these aren't such an issue since a link line or
whatever is just going to ignore any stale files anyway but with
Java you can't easily calculate all the possible .class files
(without recompiling the source) so you just grab all the files in
the directory when creating a jar or module, so you don't want
stale ones lying about.
So far i've created a tool called ijavac that uses
the --module-source-path only to automatically find
all source files that need recompiling. It optionally supports
per-module mode where it restricts processing to in-module
classes. It also automatically removes all stale files before
they are recompiled. It works by parsing all the existing .class
files, matching them up with their source based
on --module-source-path and checking timestamps. The
parsed .class files are used to create the full set of down-stream
dependent classes, then match them to the corresponding set of
.java files, and then invoke javac with this set.
In per-module mode it isn't quite as fast as using javac -m, but
it's close and it ensures stale files are removed. Because it's
only performing file-level dependencies it can recompile more than
is necessary. In whole-project mode it depends on what was
changed and how many files could need recompiling. However i'm
not sure I can fit this in with my build system as I want to
support generated files which may require a per-module build
order.
There are also cases where module mode fails, regardless of
whether the stale files are removed or not. For example:
// module a
public class Bob {
int x;
}
// module b
public class Foo {
Bob bob;
int baz() {
return bob.x;
}
}
If x is renamed in class Bob then a per-module rebuild will only
rebuild Bob.class. Subsequently running a dependency-aware module
build on module b will not recompile Foo.
The whole-project mode will catch this case succesfully assuming a
per-module build hasn't already updated Bob.class independently.
Although if you have a deeply dependent object (that is used
widely in a project) it's about the same speed just to delete all
the classes and rebuild them all together.
The main reason is that the per-module mode restricts it's view to
only in-module classes and sources. I guess it should be able to
handle cross-module checks with some additional work.
Another idea i'm toying with is creating a cleanup routine that is
run as a post-process after javac -m. Becasue this
only needs to match each .class with a .java it doesn't have to
worry about building the whole dependency graph and can get away
with only parsing the Source attribute. I'm not sure why javac -m
doesn't expunge stale files but alas it does not.
I also have the code to generate the module-level dependency lists
which is what would go into a makefile. The makefile wouldn't
track .class files as one would with C.
But for now i'm not sure I really got anywhere so I guess it'll
just go on the backburner again.
Apparently 'best practice' using maven is just to delete and
rebuild every time which is nonsense.
Kinect2 device for FFmpeg, Microsoft Kinect for Windows SDK 2.0
So further on the previous post about Kinect for Microsoft Windows
v2 support in ffmpeg ...
- My patch to ffmpeg-devel was completely ignored. Not even the
courtesy to say it wasn't welcome due to it being obsolete
hardware or any other comment whatsoever.
- My patches to libfreenect2 also seem to have been simply
ignored.
- I couldn't get libfreenect2 to work on microsoft windows 10.
It compiles and in some cases detects the camera but bulk
transfers always timeout. I tried everything!
- Using the libusb.dll in the binary download. This detects
but transfers timeout.
- Using visual studio to compile the libusb.dll. Doesn't
work at all.
- Using visual studio to compile libfreenect2 and a very
basic capture program but uses the libusb.dll from
libfreenect2 distribution. This only works if i put a couple
of Sleep() calls in the right place. Otherwise it also fails.
- Adding Sleep() calls in the ffmpeg module just times out.
- So I wrote a C dll to wrap the microsoft sdk so it could be
called from gcc compiled code as c++ has no ABI so there it can't
call it directly.
- Then I wrote another simple ffmpeg device 'kinect2' which uses
this C dll to capture on a microsoft platform.
- Due to delays in processing this locked up the capture when
trying to record all streams so I needed to use a capture thread
and dump copies of the frames to a limited-size write queue.
This works and is stable but is microsoft platform only. The
colour signal comes through as YUYV so it needs to be recompressed
for saving vs the libfreenect2 indev which supported raw jpeg
capture, so it takes considerably more cpu resources using a
software codec. Also the C dll can only be compiled with visual
studio as the Kinect headers (apart from being an auto-generated
unreadable mess) are are not standard C or c++ compatible. But
ffmpeg is still cross-compiled from a proper development system.
The c++ kinect sdk isn't too bad - apart from all the COM
overheads and unredable headers. The documentation is abysmal.
This is the first time iv'e ever used visual studio for C or c++,
and hopefully the last, it's pretty pants.
Given my shitty experience with ffmpeg-devel I probably wont
bother even submitting a patch for it there. If I decide to
publish it at all I might send a link to ffmpeg-devel just to get
some exposure.
I've found that it's almost impossible to find this site with any
search engine even if you look for something specific so it's
pretty pointless publishing it here anyway. Yesterday I was forced
to login to bing and google's search consoles to find out what the
hell was going on. bing has only indexed about a dozen pages and
google has indexed the site but barely ever shows anything, and
some of what it shows (10+ pages in) is dead links from previous
iterations of the blog software. A few months ago I added jjpeg
and zcl (at least) to the GNU Free Software Directory ... and even
there the jjmpeg entry has been sitting at 'not approved' ever
since and doesn't show the anything unless you dig further.
I've seen people asking on the microsoft developer forums for a
piece of software which does exactly this - mostly from academic
users - but if they can't find it what's the bloody point?
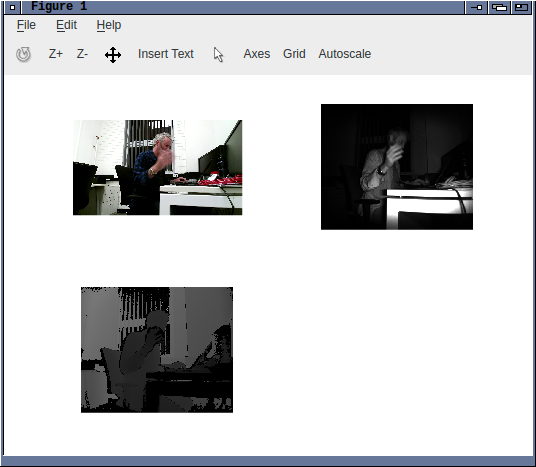
Kinect2 device for FFmpeg, libfreenect2
I've been working on a kinect2 device backend for FFmpeg the last
few days. Actually it's only about a day's work so far and i've
got the code talking to the c++
(sigh) libfreenect2,
building, and most of the glue written - I just haven't tested it
with the hardware yet. I hope it should be quite straightforward
but FFmpeg is a fairly complex library and there are a lot of
details that could be wrong.
One feature it has is that the jpeg frames are not decoded; which
means cheaper recording and no loss of capture quality. I had to
make some minor modifications to libfreenect2 for this to be possible.
It exports 3x streams: the RGB data as jpeg, the IR data as
grey16, and the depth data as grey16. I have options to enable
various subsets of these streams, so for example depth+ir decoding
can be skipped as it requires a good amount of flops. Cameras are
referenced by serial number or index. Device queries work as do
some basic capture settings. I'm also considering other options
which libfreenect2 provides such as streams with the depth/rgb
aligned to each other.
Once I have it at a working state and ported to git head (FFmpeg
git was down when i started working on it) I will see if FFmpeg is
interested in it. The fact that it requires c++ and a patched
libfreenect2 might be a downside but there is already a c++ device
in the source tree. Otherwise i'll just upload it
to code.
This was going to be for work but they decided they'd rather use
some junk matlab (ffs) on a shit platform (fffs) so i'm a little
annoyed about the whole thing. While it should be possible to get
this to work on their chosen shit platform as well it's a bit more
involved.
Parallel Streams, Blocking Queues
I've been using Java Streams a bit to do various bits of work.
One useful feature is the ability to go wide using parallel
streams. But I've often found it doesn't perform all that well.
- It only uses one thread per cpu thread so i/o heavy tasks are
underworking the machine;
- fork/join breaks work up by powers of 2 and not all jobs fit
this very well;
- Although it uses work stealing it is still basically
statically scheduled;
- Overheads.
I have written a Stream Parallel.map(Stream,
Function) call which wraps a stream mapping process in a
one that farms it out to a pool of threads and recombines it
afterwards. This works well for some tasks particularly as you
can set the number of threads, but it is still quite coarse and
you can't recursively call it (actually you can, it just launches
lots of threads).
Anyway so i'm trying to think of a way to break up multiple levels
of parallel streams into smaller blocks of tasks that can be more
freely scheduled. Whilst trying to fit it within the Stream
processing model which is pull oriented.
I'm still nutting out the details but for now I have written a
lockless, bounded, blocking, priority queue. It only supports a
fixed set of discrete priority levels.
I did some micro-benchmarks against ArrayBlockingQueue (without
priority) and i'm surprised how well it worked - from about 5x to
20x faster depending on the contention level.
Each priority level has it's own lockless queue implemented using
an array and 3 counters. The array is accessed using cyclic
addressing so all operations are O(1).
static class Queue<T> {
volatile int head;
volatile int tail;
volatile int alloc;
final T[] queue;
}
The trick is that it doesn't implement any waiting operations
because it uses external arbitration to avoid the need to.
This makes put() particularly simple. I'm using
pseudo-code atomics below, but these are implemented using
VarHandles.
void put(T value) {
int a = atomic_inc(alloc);
int b = a + 1;
volatile_set(queue, a & (queue.length-1), value);
while (!atomic_cas(head, a, b))
Thread.onSpinWait();
}
First, the allocation cannot fail and simply assigns a working
slot for the new item. The item is then filled and then the
atomic_cas() (compare-and-set) is used to ensure that the head
pointer is incremented sequentially regardless of the number of
threads which reserved slots.
The poll() method is slightly more complex.
T poll() {
int h, n, t;
T node;
do {
t = tail;
h = head;
if (h == t)
return null;
node = volatile_get(queue, t & (queue.length - 1));
n = t + 1;
} while (!atomic_cas(tail, t, n));
return node;
}
First it checks it the queue is empty and if so simply exits. It
then takes the current queue tail and then updates the tail
counter. If the tail pointer changed because
another poll() completed first, then it just retries.
The order of reading the head and tail counters is important here!
If tail is read second it is possible to double-read the same
value.
This isn't a full queue implementation as a number of important features still missing:
- Limiting the number of put()s so that the queue isn't overwritten;
- Blocking on full-write when the queue is full, without busy-waiting;
- Blocking on empty-read when the queue is empty, without busy waiting.
All of these can be almost trivially implemented using a pair of
Semaphores and an atomic integer.
- A sempaphore with (queue.length-1) reservations limits put()
calls. A successful poll releases a reservation.
- The first semaphore does this as well.
- An atomically updated counter and another semaphore is used to
implement wake-up on empty-read.
It's a bit tricky to benchmark and the results are quite noisy
despite setting the CPU to a specific (low) clock speed.
But in general this is around 10x faster than using
ArrayBlockingQueue for "low-contested" situations (6x writers, 6x
readers on a 12x thread cpu). In a "high-contested" situation
(32x writers, 32x readers), it's more like 15-20x faster, and
scales better. Despite tight loops the ArrayBlockingQueue is
unable to saturate the CPU resources (via top) and much of the
time is spent in overhead (?somewhere?). Profiling in netbeans
didn't offer any particular insight on where.
These are of course highly-contrived situations but the
performance was a pleasant surprise. It might not work on systems
with a weaker memory model than AMD-64 but I don't have access to
such exotic systems.
This still doesn't solve the base problem I was working on but
it might be a useful part thereof.
jjmpeg callbacks
Well I went and sorted out the AVIOContext callback code rather
than posting the previous post so there is more of a gap than the
date would imply ...
It turns out my idea to pass a reference to this to
open2() was a bit dumb! Because of
course open2() is the routine which creates the
pointer that this refers to in the first place.
Wrong!
Anyway the weak references were on the right track, and once I got
it working further testing showed that I had to use a weak
reference for the custom i/o handlers as well. In many cases it
would still have worked but if you created a non-static anonymous
class inside a method which stored the AVIOContext as a member
variable then it would leak all three objects. A non-static
anonymous inner class keeps a reference to this, which keeps a
reference to the AVIOContext which keeps a reference to the
non-static anonymous inner class.
So anyway the C now just uses weak references and the Java has a
holder for the AVIOInterrupt or AVIOHandler object with which it
is associated and some exploratory testing seems to confirm it
works as expected.
I reverted the nativez changes too, the reference holder wasn't a
completely terrible idea but it was duplicating existing JVM
functionality unnecessarily.
Copyright (C) 2019 Michael Zucchi, All Rights Reserved.
Powered by gcc & me!