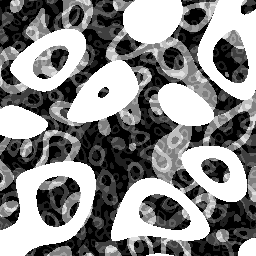About Me
Michael Zucchi
B.E. (Comp. Sys. Eng.)
also known as Zed
to his mates & enemies!
< notzed at gmail >
< fosstodon.org/@notzed >

Too noisy
Been playing a bit with simplex noise. Interesting how much you can create from the same basic function and kind of cathartic and easy on the brain.
The following were all created with the same basic noise. 4 frequencies are combined in different ways. I'm using Z as an animator so they all smoothly animate.
Blobs of liquid. This uses max(). The frequency is the same for each layer by the amplitude is altered. Note that this is purely 2D and the depth appears due to attenuation.
Smoke or writhing organic mass. This uses max(abs()) and a lower frequency.
Lava lamp ringlets. Scales to an integer and selects one of the bits from the integer. Again the depth is from attenuation and scaling in this case.
Friesian cow-hide. Or a coastline. Or a burning piece of paper. Threshold with multiple frequencies. Works very nicely as a blending mask for image transition.
I've mostly been playing with the hash function to try and create something epiphany efficient whilst still working sufficiently well. For 3D noise the current candidate uses 3 lookup tables to provide a basic hash of the x/y/z locations and they are combined using floating point multiplies and/or other bit ops. I'm only using random values which works most of the time although a better choice should be possible. It may be worth just going back to the permutation array of the original code as I realised I can implement that in only 256 bytes if i need to. I still don't know how it will run on the machine as the simplex setup code is pretty expensive too but I haven't looked at how to optimise it yet. Originally I was looking at the 2D noise because it was simpler but as 3D noise is just so much more useful I will target that instead.
I also created a 16-element spherical set of vectors for the base noise gradients. First I used an inscribed cube and some others I made up but then I finally found the code by Jon Leech (hint: it's at the bottom of the page!) which models electron repulsion to try to evenly space the points across the sphere. This does create a nicer result. 16 is used since it's a lot easier to calculate the modulus of 16 than it is for 12.
I do see patterns showing up particularly with the ringlet algorithm - lines at 45 degrees showing up as you zoom out - but this shows up for the original too. The noise is definitely not zero-mean. If I average over many frames I get fairly regular blobs at 45 degrees showing up also - although they are at 90 degrees to the ones that show up zoomed out, but again this is also present with the original Simplex noise hash function and gradient set.
"Sentinel Saves Single Cycle Shocker!"
Whilst writing the last post I was playing with a tiny fragment to see how just testing the edge equations separate to the zbuffer loop would fare. It's a bit poor actually as even the simplest of loops will still require 9 cycles and so doesn't save anything - although one wouldn't be testing every location like this so it's pretty much irrelevant.
Irrelevant or not I did see an opportunity to save a single cycle ...
If one looks at this loop, it is performing 3 edge equations positive tests and if that fails it then has to perform a loop-bounds test.
0000015e: orr.l r3,r18,r19 /| 1 |
00000162: fadd.l r18,r18,r24 \| 1234 |
00000166: add.s r0,r0,#0x0001 /| 1 |
00000168: fadd.l r19,r19,r25 \| 1234 |
0000016c: orr.l r3,r3,r20 /| 1 |
00000170: fadd.l r20,r20,r26 \| 1234 |
00000174: bgte.s 0x0000017a | 1 |
00000176: sub.s r2,r0,r2 | 1 |
00000178: bne.s 0x0000015e | 1 |
On in C.
for (int x=x0; x < x1; x++) {
if ((v0 >= 0) & (v1 >= 0) & (v2 >= 0))
return x;
v0 += v0x;
v1 += v1x;
v2 += v2x;
}
Problem is it needs two branches and a specific comparison check.
Can a cycle be saved somehow?
No doubt, don't need Captain Obvious and the Rhetorical Brigadettes to work that one out.
Just as with the edge tests the sign bit of the loop counter can be used too: it can be combined with these so only one test-and-branch is needed in the inner loop. After the loop is finished the actual cause of loop termination can be tested separately and the required x value recovered.
It's not a sentinel it's just combining logic that needs to be uncombined and tested post-loop in a similar way to a sentinel.
000001ba: orr.l r3,r18,r19 /| 1 |
000001be: fadd.l r18,r18,r24 \| 1234 |
000001c2: sub.s r0,r0,#0x0001 /| 1 |
000001c4: fadd.l r19,r19,r25 \| 1234 |
000001c8: orr.l r3,r3,r20 /| 1 |
000001cc: fadd.l r20,r20,r26 \| 1234 |
000001d0: orr.s r1,r0,r3 | 1 |
000001d2: blt.s 0x000001ba | 1 |
Or something more or less the same in C with the pro/epilogues and probably broken edge cases:
int ix = x1 - x0 - 1;
while ((v0 >= 0) & (v1 >= 0) & (v2 >= 0) & (ix >= 0)) {
ix -= 1;
v0 += v0x;
v1 += v1x;
v2 += v2x;
}
if (ix >= 0) {
return x0 + ix;
}
I suppose it's more a case of "Pretty Perverse Post Pontificates Pointlessly!"
Or perhaps it's just another pointless end to a another pointless day.
Might go read till I fall asleep, hopefully it doesn't take long.
ezegpu stuff
Did a bit more playing around on the ezegpu. I think i've hit another dead-end in performance although I guess I got somewhere reasonable with it.
- I re-did the controller so it uses async dma for everything. It didn't make any difference to the performance but the code is far cleaner.
- I tried quite a bit to get the rasteriser going a bit faster but with so few cycles to play and all the data xfer overheads with there wasn't much possible. I got about 5% on one test case by changing a pointer to volatile which made the compiler use a longword write. I got another 5% by separating that code out and optimising it in assembly language using hardware loops. This adds some extra overhead since the whole function can't then be compiled in-line but it was still an improvement. However 5% is 40s to 38s and barely noticeable.
This is the final rasteriser (hardware) loop I ended up with. The scheduling might be able to be improved a tiny bit but I don't think it will make a material difference. This is performing the 3 edge-equation tests; interpolating, testing and updating the z-buffer; and storing the fragment location and interpolated 1/w value.
d8: 529f 1507 fsub r2,r44,r21 ; z-buffer depth test
dc: 69ff 090a orr r3,r18,r19 ; v0 < 0 || v1 < 0
e0: 480f 4987 fadd r18,r18,r24 ; v0 += edge 0 x
e4: 6e7f 010a orr r3,r3,r20 ; v0 < 0 || v1 < 0 || v2 < 0
e8: 6c8f 4987 fadd r19,r19,r25 ; v1 += edge 1 x
ec: a41b a001 add r45,r1,8 ; frag + 1
f0: 910f 4987 fadd r20,r20,r26 ; v2 += edge 2 x
f4: 047c 4000 strd r16,[r1] ; *frag = ( x, 1/w )
f8: 69ff 000a orr r3,r2,r3 ; v0 < 0 || v1 < 0 || v2 < 0 || (z buffer test)
fc: 278f 4907 fadd r17,r17,r23 ; 1/w += 1/w x
100: 347f 1402 movgte r1,r45 ; frag = !test ? frag + 1 : frag
104: 947f a802 movgte r44,r21 ; oldzw = !test ? newzw : oldzw
108: 90dc a500 str r44,[r12,-0x1] ; zbuffer[-1] = zvalue
10c: b58f 4987 fadd r21,r21,r27 ; newz += z/w x increment
110: 90cc a600 ldr r44,[r12],+0x1 ; oldzw = *zbuffer++;
114: 009b 4800 add r16,r16,1 ; x += 1
Nothing wasted eh?
Using rounding mode there are I think 4 stalls (i'm not, but i should be). One when orring in the result of the zbuffer test and three between the last fadd and the first fsub. Given the whole lot is 10 cycles without the stalls that doesn't really leave enough room to do any better for the serial-forced sequence of 2 flops + load + store required to implement the zbuffer. To do better I would have to unroll the loop once and use ldrd/strd for the zbuffer which would let me do two pixels in 30 instructions rather than one in 16 instructions. It seems insignificant but if the scheduling improved such that the execution time went down to the ideal of 10 cycles and then an additional cycle was lopped off - from 14 to 9 cycles per pixel - that's a definitely not-insignificant 55% faster for this individual loop.
The requirement of even-pixel starting location is an added cost though. Ahh shit i dunno, externalising the edge tests might be more fruitful, but maybe not.
- I did a bunch more project/cvs stuff; moving things around for consistency; removing some old samples, fixing license headers and so on.
- I tried loading another model because I was a bit bored of the star - I got the Candide-3 face model. This hits performance a lot more and the ARM-only code nearly catches up with the 16-core epiphany. I'm not sure why this is.
Although there are some other things I haven't gotten to yet i've pretty much convinced myself this design is a dead-end now mostly due to the overhead of fragment transfer and poor system utilisation.
First I will put the rasterisers and fragment shaders back together again: splitting them didn't save nearly as much memory as I'd hoped and made it too difficult to fully utilise the flops due to the work imbalance and the transfer overheads. I'm not sure yet on the controller. I could keep the single controller and gang-schedule groups of 2/3/4 cores from the primitive input - i think some sort of multiplier is necessary here for bandwidth. Or I could use 3 or 4 of the first column of cores for this purpose since they all have fair access to the external ram.
simplex noise, less memory
I thought i'd look at something a bit different today: noise. Something to get the fragment shaders doing some more work.
I've looked at some of this before but it's been a while and never had much use for it.
I started with "wavelet noise" but when I realised it needed big lookup tables I went back to looking at the simplex noise algorithm. It seems wavelets are being used to create bandwidth limited versions of existing noise so that it scales better; but this isn't something I need to worry about.
A paper and implementation by Stefan Gustavson and others pretty much had me covered but I wanted to try and remove the 512+256 element lookup tables used to hash the integer coordinates to save some memory on the epiphany.
I came up with two working solutions in the end.
The first one uses a 32-element lookup table of prime numbers to implement a 2D hash function. I just grabbed the first 32 primes (20 apart) for the table and fiddled with eor/mul and shift until I had something that seemed to work. I arbitrarily chose 32 because it was a nice round number.
// there's nothing particularly good or useful here
static final int[] hasha = {
71, 173, 281, 409, 541, 659, 809, 941,
1069, 1223, 1373, 1511, 1657, 1811, 1987, 2129,
2287, 2423, 2617, 2741, 2903, 3079, 3257, 3413,
3571, 3772, 3907, 4057, 4231, 4409, 4583, 4751
};
private static int hash16(int a, int b) {
return ((((b ^ hasha[a & 31]) * (a ^ hasha[b & 31])) >> 5) & 15);
}
Because I was only interested in the 2D case I changed the gradient normal array to 16 elements so I didn't have to modulo the result as well. TBH it's kind of surprising it works as well as it does since hashing numbers is pretty tricky to get right and I really didn't know what I was doing.
When I started I didn't realise exactly what it was for so once I had a better understanding of why it was there I thought i'd try an existing integer hash function. In general they failed miserably but I found one that came from the h2 database which worked sufficiently well.
private static int hash(int x) {
x = ((x >> 16) ^ x) * 0x45d9f3b;
x = ((x >> 16) ^ x) * 0x45d9f3b;
x = ((x >> 16) ^ x);
return x;
}
private static int hash16(int a, int b) {
return (hash(a * b + a + b)) & 15;
}
I used the (a*b+a+b) calculation to turn it into a 2D hash function.
So this final version requires no lookup table for the gradient table permute at all - nice. But it requires 3 integer multiplies - not so nice for epiphany. And even the other version needs an integer multiply and thus the same costly fpu mode changes on epiphany.
Since I only need a limited number of output bits it might (should?) be possible to change this to using float multiplies to avoid the costly mode change; but this is something for further study. The first version might make this easier.
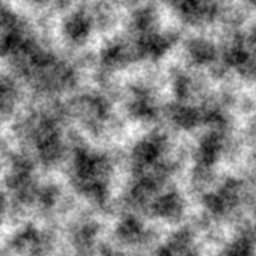
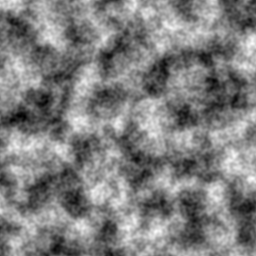
Screenshots ... this first is a simple 4-octave fractal noise generated using the 2D Simplex Noise code from Stefan. I think the 2D noise function has a small bug because it's using the 12-point 3D gradient bases which don't always evaluate to vectors of the same length in 2D but it isn't apparent once fractal noise is generated as here.
The next one is an example using the naive hash function (it may be a different scale to the others since I ran it separately). Covering 4 octaves hides some problems it might have but I've done some very basic testing to larger scales and it seems about as stable and nicely random as the others.
And the final shot is using the M2 hash function and 16 gradients evenly spaced around the unit circle rather than 12 evenly spaced around the unit sphere as in the traditional version.
Look about the same to me?
I don't know if it's useful for anything I might do or if it is even fast enough to run in a shader on the epiphany but I learnt a couple of interesting things along the way.
ezegpu
I've been doing some little bits and pieces on the ezegpu code as well.
- Changed the way async dma works in ezecore so that you can use either dma channel, enqueue your own DMA blocks and chains, and increased the queue length for more outstanding requests. I kept the old api compatible and interoperable;
- Fixed the rasteriser to use this new queue;
- Added some async dma to the controller but until everything uses it it wont pay off. It got messy enough that I need to redo it with the new goal in mind, it's not much code but I haven't gotten to it yet;
- Made the backends open the framebuffer so the same 'gles2 demo' can run against different backends by just relinking them so as to simplify comparisons;
- Added a NEON matrix multiply - it's 3x to 5x faster than a C version;
- Added a NEON scale+clamp RGBA float to byte for the all-ARM version. This is 3x faster than the C version although i've got the channels messed up so the colours are wrong;
- Did a bunch of cvs + code management stuff.
Together the NEON changes amount to a 6% improvement to the total runtime of the all-ARM code for my current testing case (8x8x8 stars). Nothing major, although it goes up on simpler scenes mostly due to the faster RGBA float to byte conversion.
egpu mk ii part 2
After a couple of days relaxing break including a nice ride down to the coast yesterday I had another look and the ezegpu today.
First task was just to create a common 'demo' frontend which can be linked to different backends so I can easily test different cases. I then created a backend based on the current mk ii state.
Well, I guess I jumped the gun a bit the other day by testing it with a poor example of large and mostly coincident triangles. Using the star-grid test the implementation is considerably faster than the line based renderer. The test code uses slightly different parameters but a 4x4x4 star test is now hitting 57fps vs 35fps for the line-based version, versus 31fps for single-core arm.
Then I upped the test to 8x8x8 stars (total of 4096 triangles) and zoomed out a bit and now the improved primitive input stage and 2d grouping really starts to show it's paces: 22fps vs 7fps. The single-core ARM code is coping a bit better at 11fps.
Well that was nice to see I guess.
I guess i'll have a look through the points of the last few posts to decide what to look at next.
some notes
Some waking up thoughts to jot down for later. It's too nice to be inside today. I have stuff I should be doing but i'm a little immobile due to hurting my foot again so I might just sit in the sun drinking. I thought it was better and over-tested it last weekend - and I wasn't even drinking :(. I can get around ok - it just doesn't heal at all if i don't rest it enough.
- Expand the state machine on the controller and make all DMA asynchronous - currently some is not.
- Use both DMA channels in the controller asynchronously, probably 0 for external reads and 1 for internal writes.
- A single non-chained DMA request can load up to two distinct objects if they are within 32K (why oh why weren't the strides 32-bit!), halving the dma request rate.
- Implement an asynchronous queue primitive combining eport + remote queue + async dma, or another primitive if it simplifies execution. For example I did manage to avoid the need for the double-dma yesterday to write the "dma complete" status on a variable-length record: I just wrote the record backwards!
- A controller for the line-mode rasteriser should significantly address the source bandwidth problem.
- Investigate synchronising the write stage to take advantage of the improved write performance of the memory interface. This probably needs to run asynchronously via interrupt code.
- The rasteriser can avoid the need to calculate the edge equations per-pixel if it knows a given region is fully in-range. This reduces the inner loop by 3 flops and 3 iops but is hard to take full advantage of due to flop latency.
- The C compiler is doing a fair job of the rasteriser loop but is still making a bit of a pigs breakfast of the address calculation. I think the 21 instructions can be reduced to 15 but to be effective I need to convert a large swathe of code to assembly.
- Use edge equations to accurately index the tiles.
- Investigate optimised renderers for special cases (for particles?). Flat shading reduces the fragment processor to a simple write (or alpha blend). Flat shading + disabled z buffer + full rectangle reduces to a simple rectangular write. etc.
- Investigate primitive synthesis on-core. e.g. particles.
I had some further thoughts on the results of yesterday; even though it's half the speed of the line renderer considering the complexity of the interactions and the forced requirement of an additional read/write cycle across another core for each fragment - it's probably actually fairly good. The main bottleneck seems to be the mismatch of rasterisation to fragment rendering time which has nothing to do with the architecture - but the fragment shaders are only trivial 3-term colour interpolations and if they were more complex then shifting the rasterisation to another core would leave more time for them to execute. So I will still hook it up to the gl frontend to test it and other backends which can use the same or similar controller setup.
Although I think due to the possibility of other highly optimised special cases a combined implementation will still be the ultimate target.
egpu mk ii.5
Well that took a bit longer than I wanted; and all i've done is rejigged all the comms around but that's enough for today.
I made a bunch of changes to address some of the problems; i'm still not sure it will fix the performance but it's some stuff I wanted to look at anyway. The big performance issue remaining is the rasteriser to fragment processor stream; I have a new communication protocol that addresses it as much as possible and have changed the fragment processor to use it but I haven't written the rasteriser to feed it yet. I was going to do a quick-and-dirty but that would just be wasted work and working toward the current target goal ended up ballooning out into a big pile of changes.
- I've changed the 4xtile geometry to 1x4 = 64x32 rather than 4x1 = 256x8. It made sense at the time. I'm hoping this simplifies the work of generating fragments in the right order but if nothing else it should divvy up the work more evenly.
- I'm probably going to interleave the 4x64x8 tiles; the whole-row rasteriser showed that this distributes the work-load more effectively than other approaches, and maybe it will simplify the rasterisation loop as it needs to interleave output for effective streaming.
- I'm creating a 2D index based on 64x64 tiles - this can be tuned a bit but very quickly chews memory depending on what limits i set (then again, that 32MB of shared ram isn't doing anything else atm). I'm just using the bounding box but it is quite simple and efficient to use the edge equations to make it exact to the index resolution.
- The controller now assigns tiles to rasterisers and dynamically schedules across all of them. This is probably the most interesting change and once I had the 2D index (which is trivial) wasn't much more work than the static assignment.
It scans across the playfield and assigns tiles to each rasteriser (3 in the current design) in turn. It then tries to keep each full of work by feeding them commands and primitives loaded from main memory using round-robin scheduling and non-blocking writes (i.e. it skips that rasteriser if it would block). If any rasteriser runs out of primitives it immediately flushes that one off and re-assigns it a new tile if there are any left - and then goes back to the stuffing loop.
I took the opportunity to batch, double-buffer, and dma everything where appropriate, and ensure that nothing can block anything else. So if this is still a performance problem I'm out of ideas. This same controller can obviously be used if the tile topology changes or if i return to unified rasterisers+fragment processors if i am ultimately unable to improve the performance of the split one sufficiently.
I've got a feeling that's where i'll end up.
- I decided to create an async dma mechanism that just stores a pointer to the dma record rather than storing dma records in-line in the queue. Only needed two changes to the assembly (shift by 2 rather than 5, change an add to ldr). I haven't tested this yet but once I have confirmed it works it's likely to replace the current async dma implementation because it can add a lot of flexibility (chained, pre-calculated, scatter-gather, etc) while retaining interoperability the current api.
I also needed a routine I could call in-line otherwise trying to call the current api from inside the rasteriser y-loop was going to spill all the registers I just spent all that code filling up with useful numbers. Since I can pre-calculate much of the DMA header into reusable blocks this should save some runtime overhead as well as I just need to update the addresses and go.
- I changed the fragment processor protocol to take specific batched blocks rather than trying to batch smaller units across a cyclic buffer. The latter is more space efficient but gets messy when using DMA to copy the blocks in. This new design simplifies some of the logic and since I need to use DMA for any non-trivial copies makes this practical to implement.
But I'm not entirely happy with the design so far though because to support asynchronous DMA operation I had to add a sentinal word which is written using chained DMA to notify the caller that it is ready. I use an eport to arbitrate the target location but it still needs to poll this ready indicator. This was the initial reason I needed the new async dma capability. Given that eports are probably going to need DMA more than I thought they would I might look at creating a combined "equeue" that hides some of these details and removes the need for the ready indicator (it can just update the remote head value).
Hmm, so what was again going to be a short little poke turned into a whole afternoon and now the sun is rapidly leaving this hemisphere to a crisp but cold evening. This stuff is just too interesting to put down and i've just spent another hour and a half writing this and tweaking a few things I found while writing it. Might keep going now ...
Update: Hacked into the later evening ... did some profiling. It's about half the speed of the combined by-line processor at this point. Whilst this is a very large improvement as to where it was, it's obviously not enough.
From some numbers I think the bottleneck is the rasteriser. The rasteriser routine is very simple and compiles quite well and the dma interface is about as minimal as possible so there is little possibility of improvement. It's probably just the 1:4 fan-out being too much.
then again ...
After the post yesterday I had a bit of a play around with the ideas. There are a couple of details I missed.
Firstly the current rasteriser implicitly maintains a per-primitive index of live pixels for the fragment processor. If I group them all together indexed (implicitly) by the column location then I have to somehow re-group the fragments afterwards so they can all be processed by the same inner loop to amortise the setup costs. After a couple of ideas I think this needs to be implemented by sorting the fragments by shader, then primitive, then X location. Because I want to leave as much processing time as possible for complex fragment shaders I was thinking of putting this onto the REZ cores; as they currently don't have a lot of work to do. This may be tunable depending on the shader vs geometry complexity.
Secondly if blending is not enabled/required then the primitives can be sorted by Z before they are sent to the epiphany; and this implicitly reduces most of the fragment processing to single pixels as well (depending on geometry) due to culling via the zbuffer test. i.e. all the work to split the fragment shaders from the rasterisers might not be much of a pay-off, particularly if it means losing 'free' alpha blending.
I did some testing using more stars (24x24x24) and found that proper z-order (front to back) makes a difference, but it's only something like 50%; but this is with a trivial fragment shader which isn't terribly representative.
Since time is not money here I'll give it a go anyway and see how it ends up. Now I write it down, restoring the primitive index by sorting would mean the same fragment processor could also support blending by just changing how and when the rasteriser outputs fragments; so I might be able to get the best of both.
I might also try changing the way the primitives are loaded in the mk i design: using (and/or dedicating) core 0,0 to load and distribute each band of primitives to the rendering engines to achieve (up to) a 16x bandwidth reduction of external reads should more than outweigh any wasted flops. I will also experiment with splitting the output into tiles instead of whole rows - the pathalogical case of a primitive taking up the whole row should be rare and if core 0,0 is handling the primitive index anyway i can add extra fidelity to the index without needing more memory to store it. I originally did rows because of the better/easier dma output and to reduce redundant setup costs and address calculations for the rasteriser, but its pretty much a wash on that front between the two approaches and 2D tiles might be a better fit.
Update: Had more of a poke today working on the setup and communications. I decided to go with tiles for the rendering off the bat because it allows more flexibility with memory: if i have a whole row in each core it forces a potentially excessively large fixed minimum size for various buffers throughout the pipeline - or an unreasonably narrow rendering resolution. But if I split it into tiles then the height can be adjusted if I need more memory. My first attempt is with tiles of 64x8 pixels which allows for a rendering width of 768 pixels if 12 cores are used for fragment shaders and only requires the same modest 8K for a 4-channel floating point colour buffer as the 512-pixel-width whole-row implementation.
I also decided to drop the fully deferred rendering idea for now - the cost of the sorting required in the rasteriser is putting me off. But It's something I can add later with most work required isolated in the rasteriser code.i
I'm still using the same topology as in the previous post with 3x rasterisers each feeding 4x fragment processors; the main driving factor for that split is the memory requirements of each stage and trying to have as many fragment processors in a round-number of cores as possible. The fact that it should route well though the mesh was mostly just a nice bonus. I'm just hoping at this point that this is also a reasonable work-balance fit as well. Because the rasteriser is going to be a fixed-function unit i'm trying to use as much of it's resources as possible, i'm sitting on around 27K of the RAM used total but I might be able to get that "a lot" higher with a bit of effort+luck.
So as of now I have a simple streaming protocol for the fragment shaders using an ezeport to arbitrate each individual fragment; this has a high(ish) overhead but it could be batched up by rows per processor. The primitive is fully rasterised across the 4 target tiles into a list of active fragments (x, y, w) - 8 bytes each. The w value of all are inverted together and then the fragments are streamed to the fragment processors with a bit of protocol compaction to reduce the transfer size and buffers required ('update y & prim id' message, 'render @ x' message). The work is streamed by row so interleaves across the 4x fragment processors - with enough buffer space (i.e. at least 64 fragments) should allow for some pipelining to hide latency across each 5-core rasteriser+fragment processor sub-system so long as the fragment shaders have enough work to perform.
Well that's where i'm at for the day. I haven't implemented the fragment shaders in the fragment processor or some of the global state broadcast from the controller. But having single messages to core 0,0 being exploded into a whole cascade of work across the mesh which is a pretty big step.
(It didn't quite go as smoothly as that suggests as I hit a bug in libezehost when dealing with heterogeneous workgroups which was a little frustrating till I worked out what was going on).
Update: Another day another bit of progress. Today I hooked up a fragment shader to the rasteriser and got it to render the single triangle test. At this point it's probably a bit slower than the previous code but there is more optimisation to be done.
I had to engineer a bit more of a streaming protocol between the rasteriser and the fragment shader; so I took the opportunity to batch up rows so they can be more efficiently written and read. I added some control codes in there as well for communicating other state and parameterising some of the processing.
I'm still not that happy with the way the rasteriser is forming the fragments: the actual rasterisation process is clean/simple but it has to output the fragments to a combined staging buffer across all tiles which must then be post-processed and broken into chunks for the 4x fragment processors. Having 4x tiles across makes the queue addressing calculation overly complex (in a loop of about 15 instructions almost anything is overly complex). As I am no longer doing deferred rendering without changing the current stream protocol it is possible to remove all the staging buffers from the rasteriser and just write directly to the stream buffers on the target cores; but I don't have a good solution yet (close though). Although i'm not sure what i'm going to do with the massive 16K x 3 this would free up!
Update: Oh damn. I tried rendering more than one triangle ... yeah its not good. Very slow proportional to the number of rendered (non-z-binned) fragments and at least for this workload the load balancing is also very bad - some cores render a ton of pixels and others render none due to the static scheduling. It looks like i miscalculated the rasteriser to fragment processor balance too; that 4x factor adds up very fast.
I went to my timing tester and did some off-core write tests: It seems i misunderstood the overhead of direct off-core writes from the EPUs - they seem to take a fixed (and unaccounted?) 9 cycles even if they "don't block". Yeah that's not going to cut it for this task. DMA seems to be able to get this down to about 1.7 cycles per float but the real benefit is that the epu runs independently and that easily outstrips the data generation rate. But it's going to need some bulky and hairy code to manage across multiple cores which is going to eat into any benefits. This definitely rules out a couple of ideas I had.
Hmm, maybe mk iii is closer than i thought. Perhaps just start with tiles so the output size is flexible and add some dynamic load balancing and a 2D primitive index. Perhaps group 2-4 cores together in terms of the front-end to try to deal with the primitive bandwidth issue; unless that upsets the balancing too much.
Copyright (C) 2019 Michael Zucchi, All Rights Reserved.
Powered by gcc & me!